Author-Veronica Davis
Last updated-Jan 22, 2026
Digital operations move quickly, and Service Request Management helps keep everyday requests organised and under control. It supports smooth handling of workflows, enquiries, and support needs across the organisation. Whether it involves onboarding a new employee, resolving a system issue, or resetting a password, this practice ensures requests move efficiently from submission to fulfilment.
In this blog, we’ll explore what Service Request Management is, why it matters, and how it supports reliable day-to-day operations. Read on to learn how to bring structure and consistency to your service delivery.
What is a Service Request?
Service request is a formal way for an employee, customer, or vendor to ask for a specific service. It is used for common, pre-approved services that are part of everyday work. For example, someone might request access to a system, new software, or equipment.
These requests follow clear steps and apply to services that are already defined. Most organisations list these services in a service catalogue, which allows users to raise requests easily through a self-service portal or service desk.

What is Service Request Management?
Service Request Management is an ITSM process for handling routine service requests in an organised and efficient manner. The objective is to simplify access to systems, tools, and support, helping everyday tasks run smoothly without disruption. By standardising request handling, IT teams can prioritise requests, automate approvals, and deliver faster, more consistent responses for end users.
Unlike Incident Management, which handles unplanned service interruptions, Service Request Management focuses on recurring activities such as granting software access, configuring devices or supplying requested information.
The Service Request Management Process
A standard Service Request Management workflow under ITIL® follows four key stages: submission and categorisation, assessment, handling and fulfilment, and closure. To illustrate the workflow, consider a scenario where a new team member, XYZ, needs access to a shared departmental network drive to perform their daily tasks. They raise a Service Request, which then moves through the ITIL® Service Request Management process:
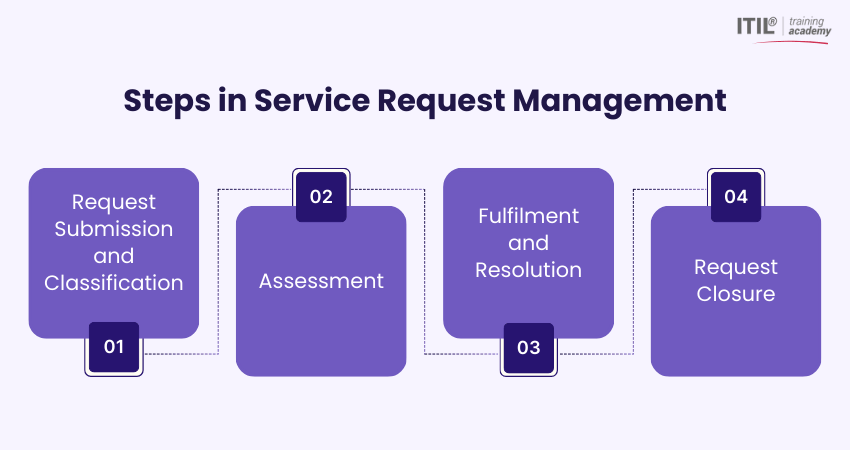
1) Request Submission and Classification
The process starts when the user submits a formal request via a service portal, email, or service desk. Once received, the request is categorised to determine its type, priority, and the team responsible for handling it.
In this scenario, XYZ submits a request through the employee portal requesting access to a shared finance drive. The system categorises it as a “File and Folder Access” request and routes it to the Access Management team.
2) Assessment
During assessment, the assigned team validates the request by checking permissions, business justification, and compliance with internal policies. Requests may also be prioritised based on urgency and workload.
Here, the Access Management team reviews XYZ's role and confirms that their job responsibilities require access to the finance drive. They also ensure the request aligns with data security and access control policies.
3) Fulfilment and Resolution
At this stage, the request is actioned in line with defined procedures. This may involve configuring permissions, updating systems, or coordinating with other teams to complete the request accurately. In XYZ's case, the team grants the appropriate read and write permissions to the shared drive and tests access to ensure it functions as intended.
4) Request Closure
The final stage confirms completion. The requester is notified, satisfaction is verified, and the request is formally closed. Resolution details are recorded for auditing, reporting and future reference. Once XYZ confirms they can access the shared drive successfully, the service desk closes the ticket and documents the outcome within the Service Management system.
Turn every ticket into a winning experience with our ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Desk Training - Sign up now!
Key Priorities in Service Request Management
A practical Service Request Management approach prioritises the customer, encourages knowledge sharing, and relies on automation to deliver consistent results. Here are some key areas IT service teams must focus on:
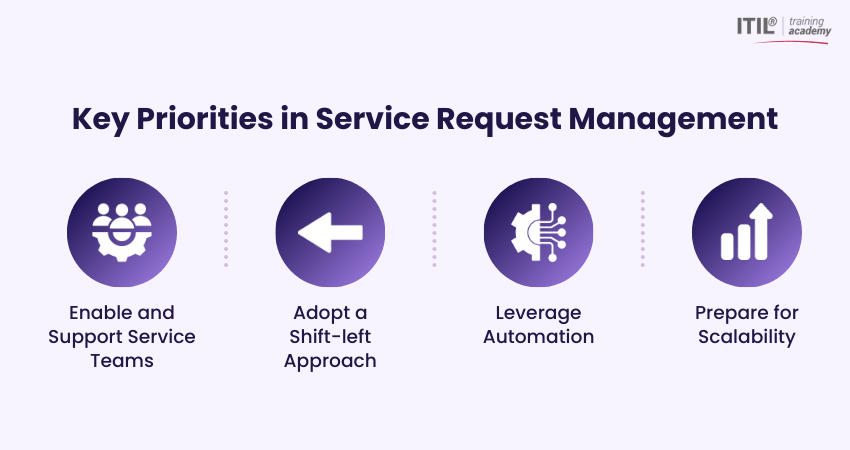
1) Enable and Support Service Teams
Improving service delivery starts with prioritising the well-being and capability of frontline support teams. Rather than relying solely on rigid escalation structures, a more collaborative Service Request Management model allows team members to work together and engage directly with users. Introducing regular retrospectives allows teams to reflect on recent requests, identify gaps and improve routing and resolution processes.
2) Adopt a Shift-left Approach
Shifting left involves moving request fulfilment closer to the point of user interaction. This approach reduces resolution times, lowers operational costs, and improves the overall user experience by resolving common requests earlier in the process.
Self-service knowledge bases, searchable FAQs and well-designed request forms help users find answers independently and provide IT teams with complete information upfront. Centralising the support experience into a single, easily accessible platform is critical.
3) Leverage Automation
Automation plays a major role in reducing manual effort and improving consistency in Service Request Management. By automating repetitive tasks such as acknowledgements and status updates, IT teams can focus on higher-value work.
Automated workflows can also route requests to the correct teams, provide standardised responses and keep stakeholders informed throughout the request lifecycle. This not only improves efficiency but also boosts transparency for users.
4) Prepare for Scalability
As organisations expand, service delivery becomes more complex, involving multiple teams and increased handovers. Without a clear structure, important context can be lost, which can slow down resolution and increase user frustration.
A well-maintained service catalogue clearly defines available services and how they can be requested. The ability to update and deploy a service catalogue quickly, without heavy technical effort, helps organisations to respond effectively to changing business requirements.
Bridge the gap between commitment and delivery with our ITIL® 4 Practitioner Service Level Management Training - Register now!
Benefits of Service Request Management
Service Request Management helps organisations track and complete requests in a clear and organised way. This makes everyday service delivery smoother and more reliable. Some of its key benefits include:
1) Standardised Service Catalogue Requests
A service catalogue clearly lists the services employees can request. It shows what is available, how long each request may take, and what information is needed. This consistent structure makes it easier to submit requests correctly and keeps the process uniform across the organisation.
2) Integrated Fulfilment Processes
Requests can be tracked from submission through completion. This keeps everyone informed about progress and helps teams use past data to set realistic timelines, costs, and service targets.
3) Complete Tracking
Service requests are linked directly to the teams and workflows that deliver them. This ensures that the requests are handled efficiently, reduces delays and supports cost-effective service delivery across the organisation.
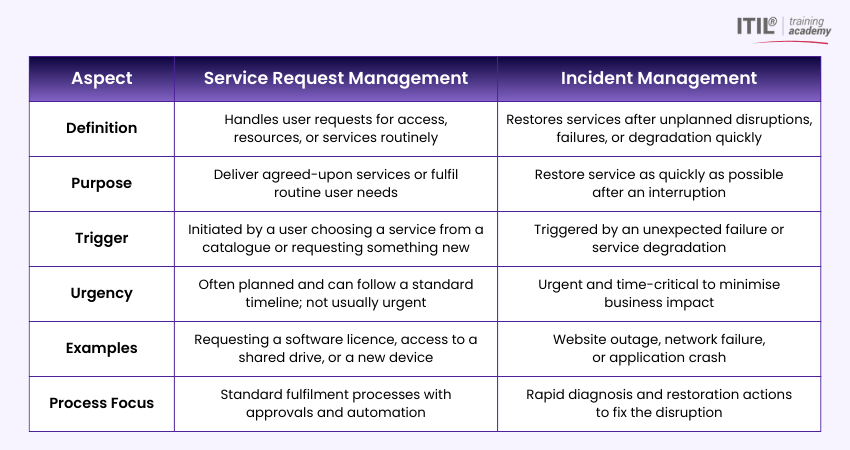
Service Request Management vs Incident Management
Here are the key differences between Service Request Management and Incident Management:
What are Examples of Service Requests?
Service requests can vary based on the services an organisation provides. Some common examples include:
1) Time-off Requests: Employees submit service requests to HR when they need to take annual leave or schedule time away from work. This helps organisations manage workloads, plan cover, and maintain smooth operations during absences.
2) Purchase Order Approvals: When teams need to buy goods or services from external suppliers, they raise purchase order requests. Finance teams review these requests to control spending and track business costs.
3) Password Resets: Password reset requests are among the most frequent service requests raised by employees and customers. IT teams typically handle these to restore secure access to systems.
4) Content Creation Requests: Departments may submit service requests when they require content for marketing, communications, or internal use. These requests are assigned to internal content teams or external partners for fulfilment.
Best Practices for Managing Service Requests
Creating a proper Service Request Management process requires thoughtful planning. Below are some proven best practices to help streamline service requests and improve service delivery:
1) Start with Simple Requests: Begin by defining the most frequent, simple, and easily fulfilled requests. This delivers quick value to users and allows IT teams to learn and refine processes before expanding the service catalogue.
2) Document Service Request Requirements Clearly: Record all request-related details, including form fields, approval flows, fulfilment steps, responsible teams, owners, SLAs, and reporting needs.
3) Collect Only Essential Information: Capture the key details required to initiate a request, but avoid overwhelming users with excessive questions. A streamlined intake improves accuracy and user experience.
4) Standardise and Automate Approvals: Apply consistent approval rules and automate them where possible. For example, routine hardware requests can be pre-approved, while software access may require Manager authorisation.
5) Define Fulfilment Ownership and Processes: Review fulfilment workflows to identify which teams complete each request and note any special requirements. Automation can help simplify and speed up these processes.
6) Support Self-service with Knowledge Content: Make sure the relevant guidance and FAQs are available across the knowledge base when a request is launched. This helps users find answers faster and reduces unnecessary requests.
7) Review and Manage SLAs: Regularly review Service Level Agreements to confirm appropriate targets, alerts and escalation rules are in place to support timely request fulfilment.
8) Track Performance with Meaningful Metrics: Identify the reports and metrics needed to manage the request lifecycle effectively. Common measures include customer satisfaction, response time, resolution time and time to close.
Conclusion
Service Request Management turns everyday requests into smooth, predictable experiences. By standardising the processes, leveraging the power of automation and keeping users informed, organisations can reduce friction and improve productivity. When done right, it speeds up delivery and ensures support feels helpful rather than frustrating.
Become the Strategist every IT team needs with our comprehensive range of ITIL® 4 Practice Manager (PM) Courses - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 28, 2026
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics