Author-Maria Thompson
Last updated-Jan 6, 2026
How do organisations ensure systems perform well, downtime is minimised, and customer expectations are met every time? This is where ITIL® Service Delivery provides clear direction, helping teams focus on delivering value rather than just managing technology.
To understand how this works in practice, this blog explores what is ITIL® Service Delivery, its foundations, key components, and best practices are. If you want to see how Service Delivery helps organisations manage services, control costs, reduce risks, and maintain continuity, keep reading.
What is ITIL® Service Delivery?
ITIL® Service Delivery refers to the set of practices that focus on delivering IT services that meet agreed business requirements and customer expectations. It emphasises reliability, quality, and value by ensuring services are available, capable, and cost‑effective.
Service Delivery defines how services are planned, delivered, monitored, and improved through clear processes, roles, and service level agreements. Its aim is to align IT services with business goals while maintaining consistent performance, managing risks, and supporting ongoing service improvement.

Foundations of ITIL® Service Delivery
Let’s look at the two core foundations of ITIL® Service Delivery:
1) The Service Management Framework
The IT Service Management (ITSM) framework provides a structured approach to planning, delivering, and improving IT services. It defines roles, processes, and practices that help IT teams deliver consistent and reliable services.
By using a common framework, organisations can align IT activities with business goals, improve service quality, and manage risks effectively. It also enables continual improvement through regular monitoring, measurement, and refinement of services.
2) Service Agreements and Customer Relationships
Service agreements, such as Service Level Agreements (SLAs), set clear expectations between service providers and customers. They define service scope, performance targets, responsibilities, and response times.
Strong customer relationships are built through transparency, regular communication, and consistent service delivery. When agreements are well managed, organisations can improve trust, reduce misunderstandings, and ensure IT services continue to meet changing business needs.
Key Components of ITIL® Service Delivery
Now, let’s look at the key components of ITIL® Service Delivery:
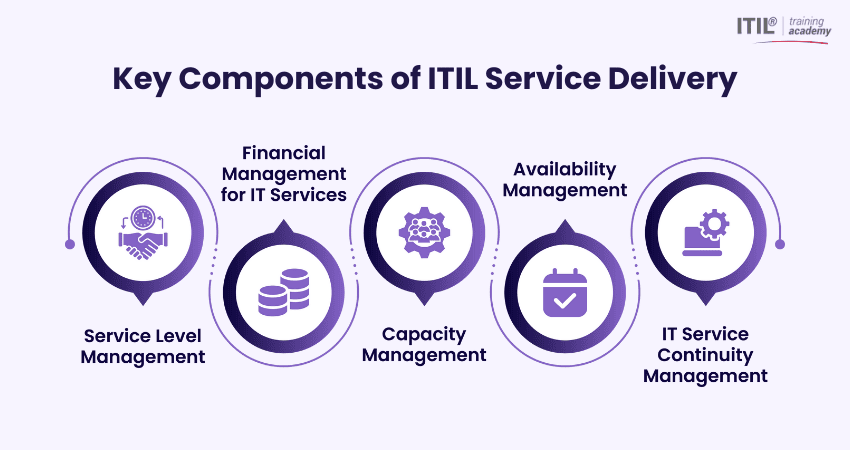
1) Service Level Management
Service Level Management defines how IT services support business goals by setting clear service expectations, responsibilities, and performance targets. It helps to align IT and business expectations, making service performance easier to measure and manage.
It covers defining service requirements, agreeing service levels, managing SLAs, and monitoring service performance against agreed targets. Using historical performance data and service reporting, teams can improve efficiency, identify trends, and plan future service improvements.
2) Financial Management for IT Services
Financial Management focuses on planning and controlling the cost of IT services to ensure spending delivers value. Its role depends on whether IT is treated as a cost centre, profit centre, or cost recovery function.
A key activity is charging, where service costs are allocated or recovered from business units based on usage. Through accurate financial data, IT teams can track service costs, support budgeting decisions, and provide transparency into the true cost of IT services.
3) Capacity Management
Capacity Management ensures IT resources are sufficient to meet current and future business demands. It helps IT teams identify potential performance issues early and plan resources proactively.
It supports infrastructure planning and application lifecycle decisions by predicting performance requirements and associated costs. Using historical data and forecasting techniques, organisations can optimise resources, reduce performance risks, and extend the effective use of existing assets.
4) Availability Management
Availability Management focuses on ensuring IT services meet agreed availability targets as defined in SLAs. It supports analysing service outages, assessing the impact of failures, and improving service reliability.
Regular monitoring, testing of resilience measures, and performance analysis help reduce downtime. With appropriate monitoring tools, teams can detect issues early, restore services faster, and minimise disruption to users.
5) IT Service Continuity Management
IT Service Continuity Management ensures IT services can be recovered within agreed timeframes following major incidents or disasters. It supports business continuity planning by aligning IT recovery priorities with business impact assessments.
Continuity plans are tailored to organisational risks such as natural disasters, cyber incidents, or system failures. Balancing recovery requirements with cost and risk tolerance helps organisations protect critical services and maintain operations during significant disruptions.
Build end-to-end ITIL® expertise with ITIL® 4 Managing Professional (MP) Certification Path – Register today!
Best Practices for ITIL® Service Delivery
Implementing best practices is essential for ensuring the ITIL® Service Delivery framework meets business and customer needs. Let's look at them below:
1) Define Business-relevant KPIs: Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that truly reflect business and service performance, such as uptime, response time, and incident resolution.
2) Implement KPI Monitoring Systems: Utilise centralised dashboards to collect and track KPI data in real time. These should be visible for both IT teams and management.
3) Align Workflow with KPIs: Design Service Delivery processes that focus on meeting agreed KPIs. Clearly define ownership and accountability for each service and performance target to maintain control and consistency.
4) Report KPIs Regularly: Review KPIs through structured service review meetings and management reports, using reliable service and infrastructure data to track trends and identify improvement areas.
5) Drive Continuous Improvement Discussions: Lead focused discussions to identify root causes. Use blameless investigations to improve operations, optimise services, and prevent recurring issues.
6) Enable Mobility and Real-time Access: Ensure KPI information is accessible on every device, including mobile platforms. This supports live visibility, faster responses, and a data-driven culture.
Conclusion
ITIL® Service Delivery provides a practical and structured way for organisations to deliver IT services. Focusing on clear service definitions, strong service agreements, measurable performance, and continuous improvements helps IT teams to support value-driven Service Delivery. This promotes a culture of improvement, transparency, and accountability to deliver a better experience for both users and businesses.
Advance your ITIL® Managing Professional skills with ITIL® 4 Managing Professional Courses today!
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics