Author-James Smith
Last updated-Dec 24, 2025
Have you ever faced a sudden system slowdown or an unexpected service outage during a busy workday? Many IT issues start small, such as a warning alert or a brief performance drop, but can quickly grow into bigger problems if ignored. This is where ITIL Event Management plays a key role, helping teams stay aware of what is happening and take timely action.
In this blog, we explore ITIL Event Management, its process, real-world examples, and best practices. Together, these areas explain how organisations can identify issues early, respond more efficiently, and deliver reliable IT services.
What is Event Management in ITIL?
Event Management in ITIL is the practice of monitoring, detecting, and managing events that occur within an IT environment to ensure services operate as expected. An event can be any noticeable change in the state of a system, service, or configuration item.
The main purpose of Event Management is to identify normal operations, highlight potential issues early, and trigger appropriate responses before disruptions occur. By filtering and analysing events, IT teams gain better visibility, reduce downtime, and support faster incident and problem resolution.
Why is ITIL Event Management Important?
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Event Management helps organisations spot IT issues early and act before they cause problems. By responding to warning signs in advance, teams keep services reliable, available, and running smoothly for users. Here are the key reasons:
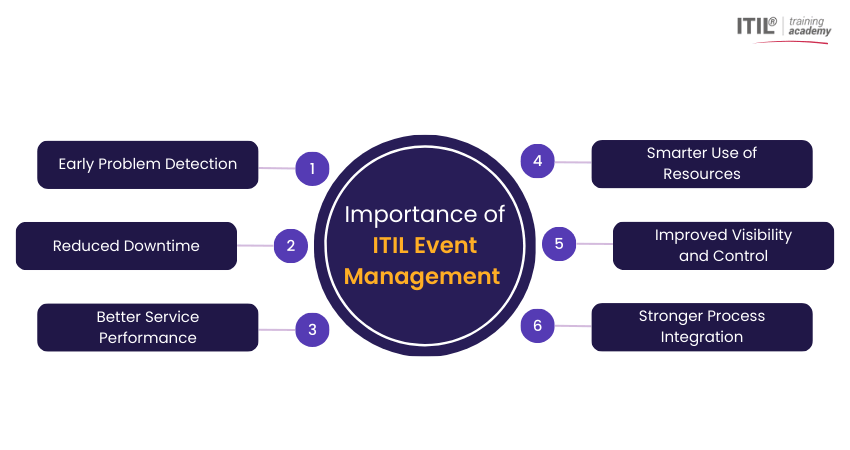
1) Early Problem Detection: Event Management helps detect potential issues at an early stage, allowing them to be resolved before they impact users.
2) Reduced Downtime: By catching issues early and using automated responses, Event Management reduces service outages and improves system uptime.
3) Better Service Performance: Continuous monitoring ensures systems stay stable and perform well, helping organisations meet service targets and user expectations.
4) Smarter Use of Resources: Automation reduces the need for manual checks, allowing IT teams to spend more time on important tasks instead of routine monitoring.
5) Improved Visibility and Control: It gives teams a clear view of system health, helping them understand what is happening across the IT environment.
6) Stronger Process Integration: When integrated with Incident and Change Management, Event Management delivers early warnings that support faster responses and better decision-making.
ITIL Event Management Process
The ITIL Event Management process follows a clear and structured flow. Each step ensures that events are handled consistently and efficiently. Here are the process steps:
Event Detection
Event detection is the first step in Event Management. It is about noticing when something changes in an IT system. Monitoring tools watch system activity, such as speed, usage, and errors, to spot events like high usage or a service stopping. At this stage, the goal is simply to recognise that an event has occurred.
Event Classification
Once an event is detected, it needs to be classified. Classification helps IT teams understand what kind of event it is and how serious it might be. There is no single correct way to classify events. Each organisation should choose a method that best supports its business needs. However, ITIL 4 commonly groups events into three types:
a) Informational Events: These show normal system activity and do not require immediate action.
Example: Recording user logins or successful backups.
b) Warning Events: These signal that something may go wrong soon if no action is taken.
Example: Server memory usage is steadily increasing.
c) Exception Events: These indicate that a service or system is operating outside acceptable limits and action is required.
Example: A service outage or a security breach attempt.
Event Prioritisation
Prioritisation helps decide which event needs attention first. It depends on how serious the issue is, how many users are affected, and how quickly it needs to be fixed. Events that affect important services are handled first. This ensures critical problems are not delayed and services remain stable.
Event Response / Resolution
Event response focuses on deciding and triggering the appropriate action, rather than fixing the issue directly. Responses may include automated actions, notifications, logging for future analysis, or escalation to Incident or Problem Management. This ensures events are handled efficiently and routed to the correct process when further investigation or resolution is required.
Develop deployment planning and coordination expertise with ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Deployment Management Training – Join now!
ITIL Event Management Examples
Below are some common ITIL Event Management examples that show how organisations help detect issues early and respond effectively.
1) Server or Network Outages: When servers or networks go down, business work can stop. Event Management helps detect outages quickly and alert IT teams, enabling faster service restoration and reduced downtime.
2) Performance Degradation: Systems may slow down without failing. Monitoring tools capture events like high CPU use or slow response times, allowing teams to fix issues early before users are affected.
3) Security Breaches or Intrusion Attempts: Events such as failed login attempts or suspicious activity need immediate action. Event Management helps detect these risks quickly and triggers responses like access blocking or security alerts.
4) Application Errors or Failures: Applications can crash or stop responding. Event Management helps identify these events early so teams can restore services and prevent repeat issues.
Challenges in ITIL Event Management
Here are the challenges that organisations must handle carefully to ensure events are managed smoothly and effectively. Here are the challenges:
1) High Volume of Events: ITIL Event Management must handle large numbers of events. Without effective filtering and prioritisation, critical exception events can be missed.
2) Insufficient Event Context: Events may lack business or service context. Limited integration with the CMDB and ITSM practices makes it harder to assess impact and urgency.
3) Overreliance on Manual Processes: Manual event handling slows response times and increases errors. ITIL encourages automation for faster and more consistent event responses.
4) Weak Integration with Other ITIL Practices: Poor alignment with Incident, Change, and Problem Management can delay escalation and create unclear ownership of issues.
5) Skills and Capability Gaps: A lack of ITIL knowledge or experience reduces the effectiveness of event classification, prioritisation, and response decisions.
6) Limited Event Review and Improvement: Without regular event analysis and reporting, recurring issues may go unnoticed, limiting continual improvement.
Boost your IT service reliability by mastering ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Problem Management Training - Join now!
Best Practices for ITIL Event Management
The following best practices help organisations manage events effectively, reduce service disruption, and improve overall service quality. Below are the key best practices for ITIL Event Management, explained in simple terms.
1) Involve Internal Experts
Even with automation, people play a critical role. Internal experts understand systems and services in detail and can help define effective monitoring thresholds and alert rules. Their input reduces unnecessary alerts and supports more accurate decision-making.
2) Ensure Teams Have the Right Resources to Respond
Monitoring tools can detect events, but people are responsible for taking action. Teams should have clearly defined roles, along with access to the tools, documentation, and information needed to respond efficiently. This helps reduce response delays and improve first-time handling.
3) Use Automation Tools as a Core Requirement
Automation is essential for managing events efficiently. It reduces manual effort, speeds up responses, and ensures consistent handling of events across systems. This allows teams to focus on complex or high-impact issues rather than routine tasks.
4) Focus on Analysing Data, Not Just Collecting It
Collecting data alone is not enough. Event analysis helps identify trends, recurring issues, and potential risks before they escalate. Regular reviews also help refine monitoring rules and improve accuracy over time.
5) Verify Monitoring Data from IT Suppliers
When IT services are managed by suppliers, they should provide clear, timely and reliable monitoring data. This ensures better visibility and supports coordinated responses to events. Well-defined agreements and responsibilities help reduce confusion during incidents.
Event Management and Technology Trends
Technology is reshaping how IT teams manage events. Modern tools help detect issues early, reduce manual work, and keep systems running smoothly. Key technology trends include:
1) Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML analyse event data to identify patterns, reduce alert noise and predict potential issues before they impact services.
2) Automation and Workflow Tools: Automation handles routine tasks like alert routing and ticket creation, helping teams respond faster with less effort.
3) Advanced Monitoring and Analytics: Real-time monitoring tools track system health and performance, helping teams identify trends and prevent issues early.
4) Cloud-based Event Management: Cloud tools allow events to be monitored from anywhere and easily scale with growing IT environments.
5) Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices generate large volumes of events. Effective event handling improves device reliability, security, and operational efficiency.
6) DevOps and Continuous Delivery: Event Management supports DevOps by monitoring frequent system changes and identifying issues during deployments and updates.
7) Event Correlation and Data Analysis: Correlating events across multiple systems helps teams identify root causes faster and avoid responding to symptoms instead of underlying issues.
8) Self-healing Systems: AI-driven automation enables some systems to resolve predefined issues automatically, reducing downtime and minimising manual intervention.
Conclusion
ITIL Event Management plays a vital role in maintaining reliable and stable IT services. By detecting events early, using automation, and integrating with other ITIL practices, organisations can reduce disruptions, improve visibility, and respond proactively. Adopting best practices and modern technologies ensures consistent service performance and continual improvement.
Advance your IT career with ITIL® 4 Practice Manager (PM) Certification and gain practical management skills today.
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics