Author-Richard Harris
Last updated-Dec 27, 2025
Technology keeps businesses running, but when systems slow down or services fail, the impact is felt immediately. From delayed work to frustrated users, even small IT issues can disrupt daily operations. This is where an IT Service Manager becomes essential, ensuring technology runs reliably behind the scenes while supporting both teams and business goals.
This blog explains the role of an IT Service Manager, required skills, salaries, and best practices in a clear and practical way. Read on to understand how this role keeps IT services running smoothly and helps organisations move forward with confidence.
What is an IT Service Manager?
An IT Service Manager is responsible for managing the end-to-end delivery, performance, and quality of IT services, acting as a link between technical teams and the business. They ensure IT services operate reliably, users are supported, and technology consistently aligns with organisational objectives.
To achieve this, they apply IT Service Management (ITSM) practices to coordinate people, processes, and technology across the service lifecycle. Frameworks such as ITIL provide structured guidance for continual improvement, helping organisations deliver consistent, value-driven IT services.
Roles and Responsibilities of IT Service Managers
IT Service Managers ensure IT services run efficiently and support business goals through planning, delivery, and continuous improvement. Their key responsibilities include:
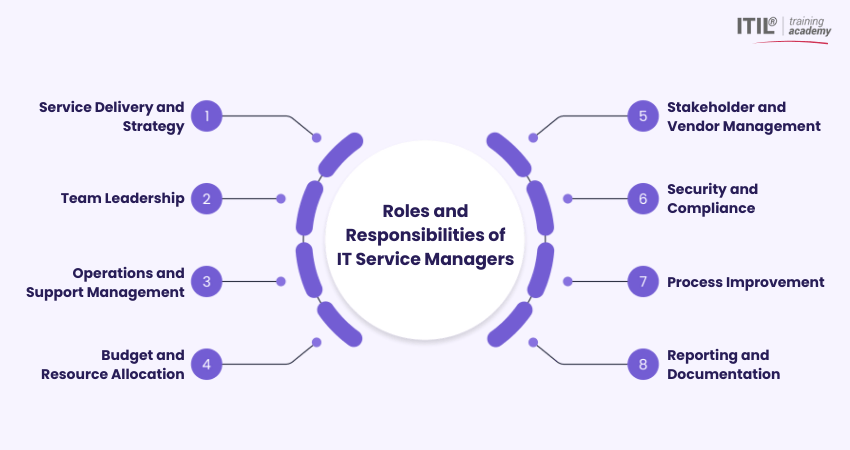
1) Service Delivery and Strategy:
Ensure IT services meet business requirements by translating organisational needs into service objectives, designing service improvements, and setting clear performance targets through Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
2) Team Leadership:
Lead, train, schedule, and develop IT teams to maintain consistent, high-quality support and service delivery.
3) Operations and Support Management:
Oversee daily IT operations, including system maintenance, incident handling, and problem management. This includes identifying root causes and maintaining service stability.
4) Budget and Resource Allocation:
Manage IT budgets, allocate resources effectively, and control operational and project-related costs to ensure cost-efficient service delivery.
5) Stakeholder and Vendor Management:
Work closely with business stakeholders to manage expectations and coordinate with third-party vendors to maintain service standards and performance.
6) Security and Compliance:
Support the implementation of security controls, promote data protection practices, and ensure IT services operate in line with regulatory and organisational requirements.
7) Process Improvement:
Review existing processes, apply ITSM frameworks such as ITIL, and drive continuous improvements to enhance service efficiency and quality.
8) Reporting and Documentation:
Prepare performance reports and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and maintain accurate documentation to support transparency, audits, and decision-making.
Build practical configuration management knowledge with ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Configuration Management Training for IT professionals – Join now!
10 IT Service Manager Skills
IT Service Managers need a balanced mix of leadership, technical knowledge, and organisational skills to manage IT services effectively. Below are the key skills required for success in this role.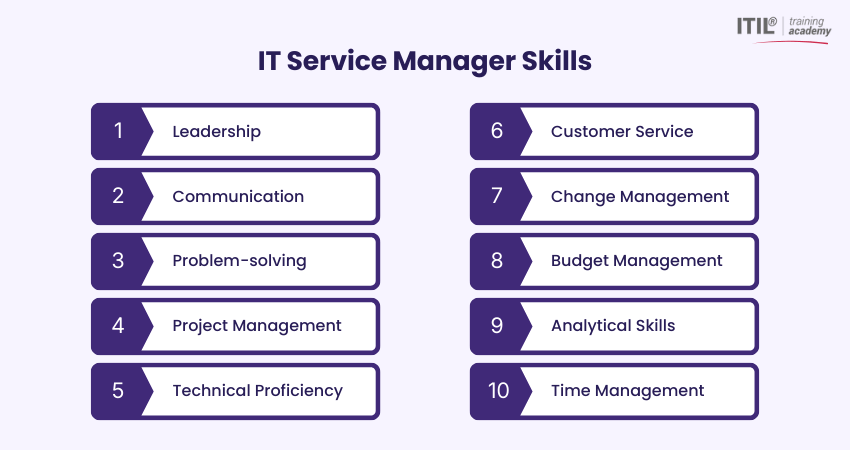
1) Leadership
IT Service Managers must lead cross-functional teams, set clear direction, and ensure accountability. Strong leadership helps motivate teams, manage conflict and drive service improvements while keeping everyone aligned with organisational goals.
2) Communication
Clear communication is essential for translating technical information into business-friendly language. IT Service Managers must communicate effectively with stakeholders, users, vendors, and technical teams to manage expectations and ensure smooth service delivery.
3) Problem-solving
When incidents or service disruptions occur, IT Service Managers must quickly identify root causes and implement effective solutions. Strong problem-solving skills help minimise downtime and prevent recurring issues.
4) Project Management
IT Service Managers often oversee service transitions, upgrades, and improvement initiatives. Project management skills ensure work is delivered on time, within scope, and with minimal disruption to business operations.
5) Technical Proficiency
While not always hands-on, IT Service Managers need a solid understanding of IT infrastructure, applications, and systems. This enables informed decision-making and effective collaboration with technical teams.
6) Customer Service
A strong service mindset is critical. IT Service Managers focus on user satisfaction by ensuring services meet agreed service levels and by continuously improving the overall user experience.
7) Change Management
Managing change effectively helps reduce risk and resistance. IT Service Managers plan, assess, and communicate changes clearly to ensure services remain stable while evolving to meet business needs.
8) Budget Management
IT Service Managers are often responsible for controlling service costs. Budget management skills help balance financial constraints with service quality and ensure value from IT investments.
9) Analytical Skills
Analysing performance data, trends, and service metrics allows IT Service Managers to make informed decisions. These skills support continual service improvement and proactive issue management.
10) Time Management
With multiple services and priorities to manage, effective time management is essential. IT Service Managers must prioritise tasks, handle incidents efficiently, and ensure long-term improvements are not overlooked.
IT Service Manager Job Description
An IT Service Manager ensures IT services support business goals by managing service quality, performance, and operations. The job description below outlines the key responsibilities, skills, and qualifications for this role.

How to Become an IT Service Manager?
Becoming an IT Service Manager requires a strong combination of education, practical experience, and continuous skill development. The key steps to follow are outlined below:
1) Academic Qualifications
Begin with a Bachelor’s degree in Information Technology, Computer Science, or a related field. Advanced education, such as a master’s degree in IT Management, can further strengthen career prospects.
2) Gain Relevant Experience
Build hands-on experience through roles such as IT Support, Network Administrator, or Systems Analyst. These positions provide valuable insight into IT operations and Service Management processes.
3) Professional Certifications
Enhance your professional profile with ITIL® certifications, which demonstrate structured knowledge of IT Service Management principles and practices. These credentials strengthen professional credibility and support career progression in IT service delivery and management roles.
4) Develop Key Skills
Focus on building essential skills such as technical knowledge, problem-solving, leadership, and communication to manage IT services effectively. These skills support informed decision-making and handling complex service challenges.
5) Networking and Mentorship
Engage with industry experts and seek mentorship from experienced IT Service Managers. Networking helps gain practical insights and opens doors to career opportunities. Mentorship also provides guidance on career growth and real-world Service Management challenges.
6) Lifelong Learning
Stay current with industry trends by attending training programmes, workshops, and webinars. Continuous learning ensures long-term success in the evolving IT Service Management field. It also helps professionals adapt to new technologies and Service Management practices.
Advance your career with ITIL® 4 Specialist Create, Deliver and Support (CDS) Training and build real‑world skills that set you apart.
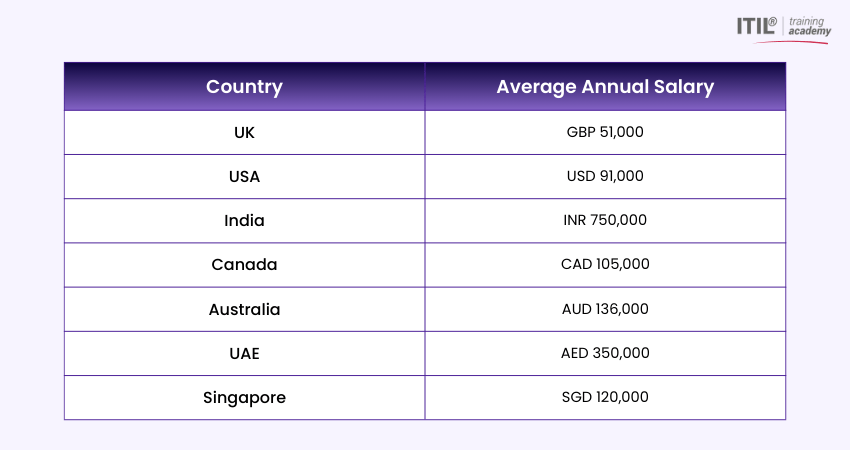
Average Salary of an IT Service Manager
IT Service Manager salaries vary by country based on demand, experience, and cost of living. The table below shows the average annual salary range for this role across key global markets.
![]() Common Challenges Faced by IT Service Managers
Common Challenges Faced by IT Service Managers
IT Service Managers work in dynamic environments where technology, business priorities, and user demands constantly change. Below are some of the most common challenges they face.
1) Rapid Technological Change
Technology evolves quickly, with new tools, platforms, and systems introduced regularly. IT Service Managers must adopt these changes while maintaining service stability, which can be challenging without disrupting ongoing operations.
2) Consistent Service Quality
Delivering consistent service quality across multiple systems and users is a key challenge. IT Service Managers must ensure services meet agreed service levels, even during incidents, peak usage, or system upgrades.
3) IT Alignment with Business Objectives
Aligning IT services with business goals requires close collaboration with stakeholders. IT Service Managers must ensure technology investments support organisational priorities and deliver measurable business value.
4) Cyber Security Risks
Cyber threats are increasing in frequency and complexity. IT Service Managers must protect systems and data, ensure compliance with security policies, and respond quickly to security incidents.
5) User Expectations
Users expect fast, reliable, and seamless IT services. Managing these expectations while working within budget, resource, and technical constraints is an ongoing challenge for IT Service Managers.
Develop advanced IT Service Management capabilities through the ITIL® 4 Managing Professional Transition Module Training – Join now!
Best Practices for an IT Service Manager
An IT Service Manager is responsible for delivering and improving IT services using IT Service Management (ITSM) practices such as incident, problem, and change management. The key practices are outlined below.
1) Service Management:
Managing incidents, service requests, problems, and changes forms the core of IT Service Management. Strong control over these processes ensures stability and quick issue resolution.
2) Service Desk and Service Delivery Management:
The service desk acts as the first point of contact for users and must be well-managed to handle requests and escalations efficiently. Service Delivery Management ensures IT services consistently meet business needs and SLAs.
3) Service Catalogue Management:
Maintaining a clear service catalogue helps define available IT services, streamline request handling, and support service continuity planning.
4) Proactive IT Management:
Proactive practices such as release, configuration, and asset management help maintain control over IT infrastructure, reduce risks, and improve system stability.
5) Service Reporting and Performance Management:
Tracking service performance through reporting and metrics enables continuous improvement, cost optimisation, and better decision-making.
6) Service Governance, Strategy, and Design:
Governance and strategic planning ensure IT services align with long-term business objectives, while service design shapes reliable and scalable service offerings.
Best Tools for IT Service Manager
IT Service Managers use ITSM tools to plan, deliver, and support IT services efficiently. These tools manage incidents, requests, changes, and performance while improving visibility and control.
1) ServiceNow: A comprehensive platform offering end-to-end ITSM and workflow automation
2) Jira Service Management: A flexible tool for service desk operations, incident tracking, and team collaboration
3) BMC Helix ITSM: An enterprise-grade solution designed for large and complex IT environments
4) Freshservice: A user-friendly ITSM platform suited for fast deployment and ease of use
5) ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus: A cost-effective solution for managing IT services and support
Choosing the right tool depends on the organisation’s size, service complexity, and budget requirements.
Conclusion
An IT Service Manager plays a vital role in keeping IT services reliable, secure, and aligned with business needs. By applying structured service practices and using the right tools, organisations can improve service quality, reduce disruptions, and deliver greater value to users in a constantly evolving digital environment.
Start your ITIL® Foundation Level Training today and build core skills for better IT Service Management success.
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics