Author-Maria Thompson
Last updated-Aug 28, 2025
Curious how Netflix stays up even when millions are streaming at once? It’s all thanks to smart IT planning and management powered by frameworks like the ITIL Service Lifecycle. This structured approach ensures IT services are strategically designed, highly reliable, and continuously improved, giving users a seamless, hassle-free experience every time.
In this blog, we’ll explore what ITIL service lifecycle is, its five stages, key benefits, and a few tips for applying ITIL effectively in any organisation.
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL Service Lifecycle?
2) The Five Stages of the ITIL Service Lifecycle
3) Benefits of ITIL Lifecycle Implementation
4) Tips for Using the ITIL Service Lifecycle
5) Conclusion
What is ITIL Service Lifecycle?
ITIL stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. ITIL Service Lifecycle is a framework that defines how IT services are planned, created, delivered, and continuously improved. It provides best practices to ensure IT services meet business objectives and customer expectations. It consists of five main stages that work together to manage the full lifecycle of a service.
The lifecycle consists of five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement that work together to improve service quality, manage risks, and maintain reliability. This structured approach helps businesses deliver greater value while staying efficient and competitive in a changing digital world.
The Five Stages of the ITIL Service Lifecycle
The ITIL Service Lifecycle is a framework with five stages that help businesses plan, deliver, and improve IT services while ensuring they support business goals. Here are the five stages:
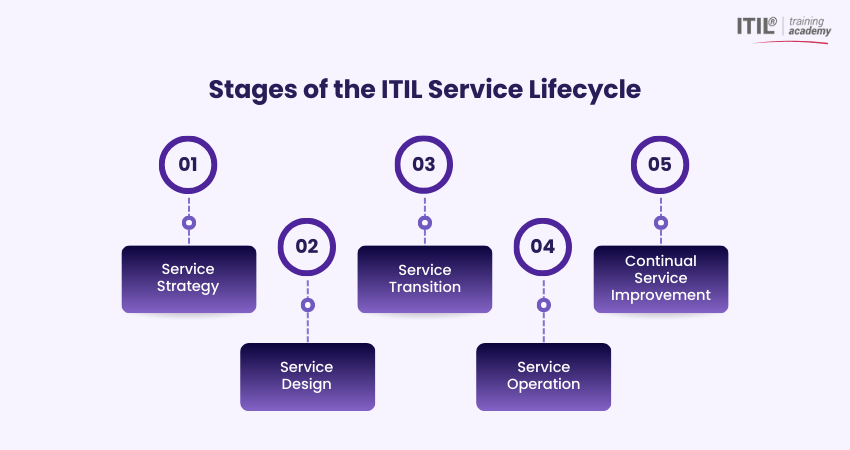
Stage 1: Service Strategy
This is the planning stage of the ITIL lifecycle. It focuses on setting a clear vision for IT services and deciding how IT will create value for the business.
a) Know customer requirements and expectations
b) Decide which services to give and why they matter
c) Plan for budgets, demand, and business priorities
d) Align IT services with long-term business targets
Example: An organisation has decided to launch a 24/7 online support system after identifying customers need for faster assistance.
Stage 2: Service Design
This stage is about designing new services or improving existing ones, so they are reliable, cost-effective, and user-friendly.
a) Design processes, tools, and systems to deliver services
b) Plan for capacity, performance, and availability
c) Ensure security, compliance, and service quality
d) Create detailed service blueprints before implementation
Example: The support system is designed to be secure, reliable, and user-friendly, with enough capacity to handle peak demand.
Streamline your service fulfilment with efficiency. Join our ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Request Management Certification now!
Stage 3: Service Transition
This stage focuses on moving services from design to live operation safely and efficiently. It ensures changes are well-tested and smoothly implemented.
a) Test the service performance and reliability before release
b) Manage risks and potential issues during deployment
c) Train employees and prepare users for changes
d) Control versions and handle Change Management properly
Example: Before going live, the system is thoroughly tested, staff are trained, and risks are managed to ensure a smooth rollout.
Stage 4: Service Operation
This is where services are delivered and managed daily. The goal is to keep everything running smoothly and solve problems quickly.
a) Monitor service performance and system health
b) Manage incidents, outages and service requests
c) Deliver technical support to the customers when needed
d) Ensure customer satisfaction with consistent quality
Example: Once live, the system is monitored daily, with the IT team resolving issues quickly to keep services running smoothly.
Stage 5: Continual Service Improvement
This stage focuses on improving IT services continuously to meet changing business requirements and customer outlook.
a) Measure service performance using data and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
b) Gather feedback from users and stakeholders
c) Identify gaps, issues, or inefficiencies
d) Make ongoing improvements to increase value and efficiency
Example: Feedback and performance data are reviewed, leading to upgrades like adding chatbots to speed up responses for common queries.
Benefits of ITIL Lifecycle Implementation
Implementing the ITIL Service Lifecycle helps businesses manage IT services better, improve quality, reduce risks, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are the key benefits of using the ITIL lifecycle:
1) Better Alignment with Business Goals
The ITIL Service Lifecycle ensures that IT services directly support business objectives. By structuring Service Management around organisational needs, companies can deliver measurable value and stay focused on their overall strategy.
2) Enhanced Service Quality and Consistency
With standardised processes, ITIL reduces errors, minimises disruptions, and ensures reliable service delivery. This helps organisations maintain high performance and build long-term customer trust.
3) Efficient Change and Risk Management
ITIL provides a structured approach to handling changes smoothly and reducing risks. Clear transition processes minimise downtime, improve service stability, and help IT teams adapt quickly to new requirements.
4) Better Resource Utilisation and Cost Control
By aligning service delivery with demand, ITIL helps optimise resource use and reduce wasteful spending. It enables better planning, prioritisation, and strategic allocation of time, money, and people.
5) Increased Flexibility and Scalability
Through regular performance monitoring and continuous improvements, ITIL makes IT services more adaptable and scalable. Organisations can easily respond to changing demands and emerging technologies while improving overall efficiency.
Enhance configuration accuracy and reliability with our ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Configuration Management Training – Join now!
Tips for Using the ITIL Service Lifecycle
The ITIL Service Lifecycle provides a clear and structured way to manage IT services, helping organisations align with business goals and continuously improve performance. Here are some key tips to make the most of it:

1) Gain a Deep Understanding of Each Lifecycle Stage
Learn about the five ITIL stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation and Continual Service Improvement (CSI). Knowing these stages helps you manage IT services better.
Example: Before launching a new online banking app, a company studies each stage to plan, design, test, and improve the app for a smooth customer experience.
2) Align IT Services With Business Goals
Make sure IT services match the company’s goals. When IT supports business needs, it improves efficiency, keeps customers happy, and adds value to the organisation. This alignment ensures IT contributes directly to overall business success.
Example: An e-commerce company introduces 24/7 live chat support because the business aims to enhance customer satisfaction and boost sales.
3) Focus on Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Always look for ways to improve services. Check performance, gather feedback, and make changes when needed to keep services effective and up to date. Regular improvements help IT stay relevant and meet changing customer needs.
Example: A video-streaming platform regularly monitors buffering issues and upgrades servers to deliver faster, smoother streaming for users.
4) Clearly Define Roles and Responsibilities
Give each person clear tasks and responsibilities. When everyone knows what to do, it avoids confusion, improves teamwork, and makes service delivery smoother. Clear roles also increase accountability and boost overall productivity.
Example: In a hospital’s IT department, one team handles patient data security, while another manages 24/7 system availability. This avoids overlaps and ensures smooth operations.
5) Leverage Automation for Efficiency
Use automation tools to handle repetitive tasks quickly. This saves time, reduces mistakes, and makes managing incidents, changes, and requests much easier. Automation also frees up teams to concentrate on more important tasks.
Example: An IT support team uses automated ticketing software to assign service requests instantly, reducing response times and improving customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The ITIL Service Lifecycle provides a clear, structured approach to managing IT services effectively. By understanding its five stages, organisations can design better services, deliver them smoothly, and continuously improve to meet changing needs. It helps businesses align IT with goals and enhance customer satisfaction. It also enables them to stay competitive in a fast-paced digital world while ensuring reliability and efficiency across all services.
Learn best practices to improve IT service delivery and management. Join our ITIL® 4 Practice Manager (PM) Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics