Author-Maria Thompson
Last updated-Sep 20, 2025
What if you could avoid half the project headaches just by thinking like a Service Manager? With ITIL Project Management, that’s exactly what you do. It’s about shifting how you approach outcomes. This blog introduces a complete, clear view of how ITIL elevates project delivery, ensures smoother transitions, and keeps services ticking long after you’ve packed up. Once you see how easily ITIL fits into your existing processes, you’ll wonder why it wasn’t always this way.
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL Project Management?
2) Key Terms in ITIL Project Management
3) How ITIL Adds Real Impact to Project Management?
4) Applying ITIL Certification Across Project Management Phases
5) ITIL in Practice: Strengthening Project Management
6) How ITIL Principles Transform Project Management Across Industries?
7) ITIL Project Management Performance Metrics (KPIs)
8) Benefits of Applying ITIL 4 Principles to Project Management
9) The Changing Role of ITIL 4 in Modern Project Management
10) Conclusion
What is ITIL Project Management?
ITIL® Project Management in ITIL 4 emphasizes aligning IT projects with business objectives to ensure efficient and effective service delivery. Projects are seen as temporary yet strategic efforts that drive value through service improvements or innovations. The approach integrates service lifecycle stages into project phases, promoting consistency and quality.
ITIL 4 also highlights the need for flexibility and continuous improvement in a rapidly changing business environment. By managing projects proactively, organizations can introduce new services, enhance existing ones, and implement solutions that improve efficiency. This ensures they remain competitive and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Process Description
ITIL® Project Management, also known as Transition Planning and Support, was introduced in ITIL® v3 to provide structured guidance for managing service transition projects. While ITIL® v2 briefly addressed project management, ITIL® v3 and ITIL® 4 offer more comprehensive support.
Though ITIL doesn’t detail full project management methodologies, it outlines key activities and interfaces with other ITSM practices. Its primary goal is to plan and coordinate resources to deliver project releases within defined cost, time, and quality constraints.
Sub-processes
Let’s explore the key sub-processes and their objectives:
1) Project Initiation:
Defines project stakeholders, responsibilities, and available resources. It also documents risks, constraints, and assumptions affecting the project.
2) Project Planning and Coordination:
Ensures service transition projects follow the organization’s project management guidelines. It coordinates activities and resources, facilitating planning across other ITIL processes.
3) Project Control:
Monitors project progress and resource usage. It aims to accelerate progress when needed and correct deviations or errors.
4) Project Reporting and Communication:
Provides a comprehensive summary of planned or ongoing service transition projects. This sub-process ensures clear communication with customers and other service management functions.
Key Terms in ITIL Project Management
Understanding ITIL Project Management requires familiarity with key terms that define its structure and intent. Terms like Service Lifecycle refer to the five core stages, Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Improvement.
Change Management focuses on controlling changes with minimal disruption, while Service Level Agreements (SLAs) set performance expectations. Configuration Management deals with tracking service assets, and Incident Management ensures rapid restoration of services. These foundational concepts help align project outcomes with IT service delivery goals.
How ITIL Adds Real Impact to Project Management?
ITIL brings immense value to Project Management by ensuring that IT services are not only delivered on time and budget but also meet business needs and quality standards. Unlike traditional approaches that focus mainly on project delivery, ITIL integrates ongoing service performance into the process.
This results in better stakeholder alignment, improved Risk Management, and long-term service success. ITIL’s structured, customer-focused approach ensures that projects add real value beyond go-live dates, making it a powerful framework for service-driven organisations.
Start building better IT services today – The ITIL® 4 Practitioner Problem Management Training gets you there.
Applying ITIL Certification Across Project Management Phases
Use your ITIL knowledge strategically at every stage of a project to improve service alignment, reduce risks, and enhance delivery quality. Below is how ITIL practices can be applied in each phase:
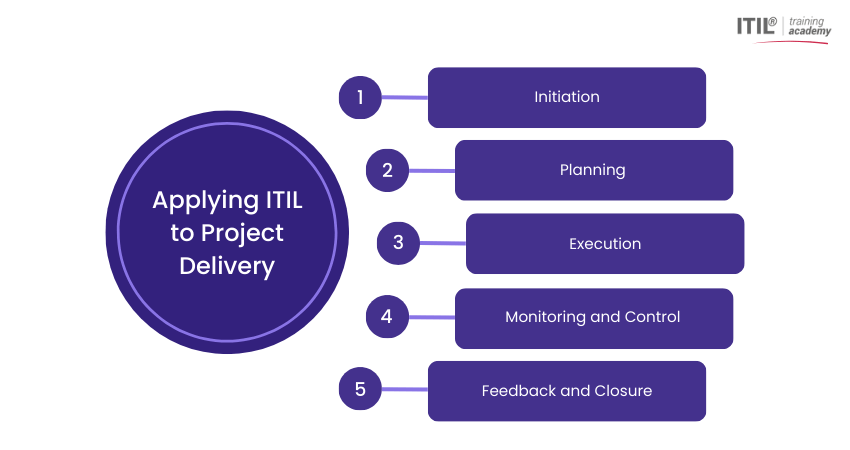
1) Initiation
Lay the foundation for service-aligned success.
a) Define Service Goals: Use ITIL’s Service Strategy principles to understand what value the project is expected to deliver to customers or users.
b) Identify Stakeholders: Clearly map out internal and external stakeholders and define their service expectations early.
c) Assess Feasibility: Apply demand and capacity management to assess whether the organisation can deliver and support the service.
Start your ITIL® 4 Managing Professional Transition Module and master the foundations of IT service excellence!
2) Planning
Prepare with clarity and service foresight.
a) Incorporate Service Design: Use ITIL’s Service Design phase to develop service architectures, processes, SLAs, and performance benchmarks.
b) Plan for Change and Releases: Define how changes will be assessed, approved, and implemented through Change Management and Release Management frameworks.
c) Risk and Compliance Planning: Integrate ITIL's availability, security, and continuity management to plan for potential disruptions and maintain compliance.
3) Execution
Deliver efficiently while maintaining service quality.
a) Service Transition Coordination: Work closely with ITIL Transition processes to ensure all service components are tested, validated, and deployed smoothly.
b) Incident and Problem Handling: Apply Incident Management to resolve delivery issues quickly and Problem Management to prevent recurring obstacles.
c) Knowledge Management: Create a repository of service-related knowledge to assist teams, reduce training time, and improve consistency.
Monitoring and Control
Track performance and adapt proactively.
a) Service Level Monitoring: Use SLAs and OLAs as benchmarks to measure service delivery performance throughout the project lifecycle.
b) Change Control Monitoring: Keep tabs on change requests, their impact, and their approval status using ITIL’s Change Evaluation process.
c) Configuration Tracking: Leverage the CMDB (Configuration Management Database) to monitor infrastructure and service components affected by project activities.
Feedback and Closure
Evaluate, reflect, and optimise future efforts.
a) Post-Implementation Review: Conduct formal evaluations to assess how well the service met its intended goals and where improvements are needed.
b) Capture Lessons Learned: Feed observations into ITIL’s Continual Service Improvement (CSI) model to refine future project and service strategies.
c) Service Handover and Closure: Ensure smooth handover to operational teams, finalise documentation, and close support-related tasks properly.
ITIL in Practice: Strengthening Project Management
Applying ITIL in real-world Project Management helps bridge the gap between delivering projects and ensuring ongoing service value. While traditional Project Management focuses on timelines, scope, and cost, ITIL brings in service-centric thinking.
By incorporating ITIL practices such as Service Strategy, Change Management, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI), Project Managers can ensure that new services are not only delivered successfully but are also sustainable long-term. It enables teams to foresee service-related risks early, integrate operational requirements during planning, and transition smoothly into support.
In practice, this means improved stakeholder satisfaction, fewer post-launch issues, and services that perform as expected beyond the project close. Whether launching a new IT system or upgrading existing services, ITIL strengthens project outcomes by making service excellence part of the core delivery strategy.
How ITIL Principles Transform Project Management Across Industries?
ITIL principles offer a structured, service-oriented approach that transforms how projects are managed, regardless of industry. While ITIL originated in IT service management, its principles of value creation, continual improvement, and alignment with business goals are now widely adopted across healthcare, finance, education, manufacturing, and more.
By focusing on customer needs, service performance, and lifecycle thinking, ITIL helps Project Managers design processes that not only deliver results but sustain them. For example, a healthcare provider might use ITIL to ensure patient-facing systems meet compliance and reliability standards. In finance, ITIL helps control risks and maintain service continuity. In retail, it ensures technology projects align with evolving customer behaviour.
From early planning to service transition and feedback, ITIL’s adaptable framework ensures smoother rollouts, fewer disruptions, and measurable value. It empowers industries to treat projects not as isolated tasks but as integrated service journeys that drive lasting impact.
Build your IT career with ITIL® 4 Managing Professional (MP) Certification Path – Learn the essentials, lead with confidence.
ITIL Project Management Performance Metrics (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in ITIL Project Management help assess the effectiveness and efficiency of project-related service delivery. These metrics ensure that both project goals and service outcomes are aligned with business expectations.
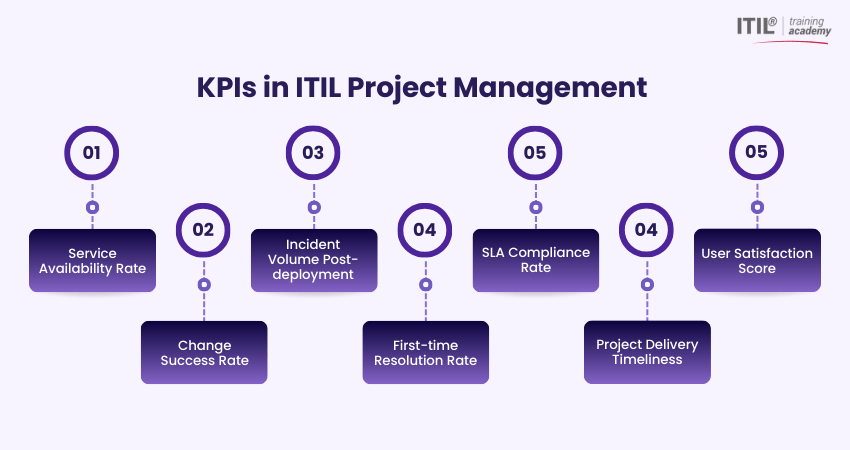
Common ITIL Project Management KPIs:
1) Service Availability Rate: Measures the uptime of critical services post-project deployment.
2) Change Success Rate: Tracks the percentage of successful change implementations without rollbacks or incidents.
3) Incident Volume Post-deployment: Evaluates the number of issues reported after the go-live phase.
4) First-time Resolution Rate: Indicates how efficiently the support team resolves incidents introduced by new projects.
5) SLA Compliance Rate: Measures how well the service meets agreed Service Level Agreements post-deployment.
6) Project Delivery Timeliness: Tracks whether the project milestones and go-live dates were achieved as planned.
7) User Satisfaction Score: Captures stakeholder or end-user feedback after project completion.
Benefits of Applying ITIL 4 Principles to Project Management
Integrating ITIL 4 principles into Project Management enhances service alignment, agility, and value delivery. It helps Project Managers focus not just on execution, but on long-term outcomes, stakeholder satisfaction, and continual improvement. With a flexible, collaborative approach, ITIL 4 ensures projects stay business-focused and adaptable across all industries.
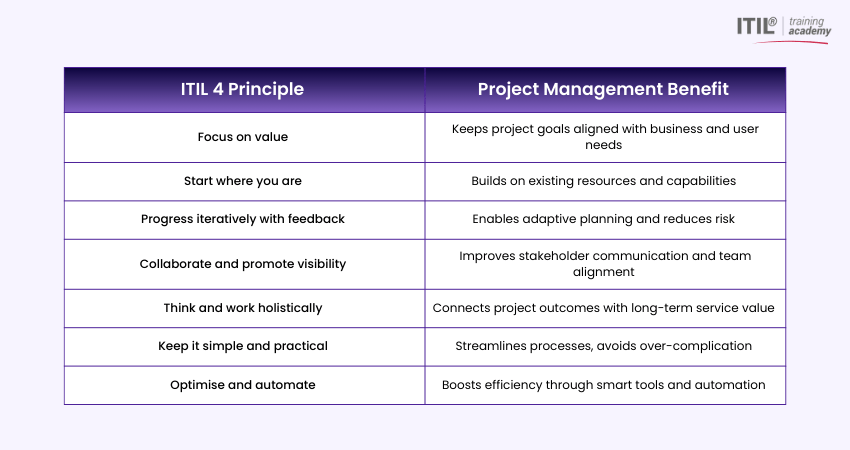
The Changing Role of ITIL 4 in Modern Project Management
ITIL 4 has redefined its role in the Project Management space by shifting from a strictly service-focused framework to one that supports agile, fast-moving, and value-centric project environments. It is no longer limited to IT service operations but is now a key enabler of effective project delivery across departments.
Key Ways ITIL 4 is Shaping Modern Project Management:
1) Supports Agile and DevOps Integration: ITIL 4 complements Agile and DevOps by allowing faster iterations, cross-functional teamwork, and continuous feedback within projects.
2) Promotes Value Creation Over Process Focus: Modern projects focus on delivering value. ITIL 4 aligns project goals with business outcomes and customer satisfaction.
3) Enables Holistic Service Thinking: Encourages Project Managers to consider the full lifecycle, from planning to ongoing service impact, when executing projects.
4) Encourages Iterative Delivery: With principles like “Progress Iteratively with Feedback,” ITIL 4 makes room for flexibility and learning throughout a project.
5) Enhances Stakeholder Engagement: The emphasis on collaboration and visibility keeps all parties informed, reducing resistance and increasing project success.
6) Bridges Strategy and Execution: ITIL 4 helps Project Managers connect high-level business strategies with on-the-ground project activities and service improvements.
Conclusion
ITIL brings clarity, consistency, and service-focused thinking to every stage of Project Management. By integrating its principles, organisations can improve project outcomes, reduce risks, and deliver long-term value. Whether you're managing IT services or business change, applying ITIL helps align goals and ensure success. Embrace ITIL Project Management to drive continuous improvement across your teams.
Upgrade your skills with ITIL® Foundation Level Training– Perfect for IT professionals and beginners alike.
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics