Author-Veronica Davis
Last updated-Sep 20, 2025
Mastering the balancing act of what customers need and what services can deliver is one of the biggest challenges for Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) professionals. This is where ITIL Demand Management comes in as the guiding light for organisations. It helps them secure the synergy of anticipating needs, aligning resources and delivering value without waste.
Far from a background function, it’s the heartbeat that keeps ITSM efficient and responsive. This blog unpacks the ITIL Demand Management principles, walks through its process, spotlights the challenges and benefits. So read on and embrace this silent engine behind seamless service delivery!
Table of Contents
1) What is ITIL Demand Management?
2) Scope of ITIL Demand Management
3) Principles and Key Concepts of ITIL Demand Management
4) The ITIL Demand Management Process
5) Benefits of ITIL Demand Management
6) Common Challenges in ITIL Demand Management
7) What Does Good Demand Management Look Like?
8) Conclusion
What is ITIL Demand Management?
The ITIL Demand Management process is aimed at anticipating customer needs and delivering services efficiently while controlling costs. It focuses on analysing, forecasting and influencing demand for products and services. It plays a pivotal role in the service strategy stage of the ITIL Service Lifecycle. This stage covers service planning, scope definition, budgeting, and other key activities.
ITIL Demand Management isn’t limited to technical capacity. It includes Human Resources, such as scaling service desk teams to address higher volumes of queries or deploying extra network staff to configure servers and hardware as demand increases.
Scope of ITIL Demand Management
The scope of Demand Management in ITIL primarily revolves around identifying and analysing business activity patterns that trigger service demand. It also involves understanding how different user groups contribute to this demand. Key activities within the scope of ITIL Demand Management include:
1) Identifying and analysing business activity patterns related to services.
2) Profiling users and studying their service usage behaviours.
3) Collaborating with Capacity Management to agree on and implement measures that can influence demand, commonly referred to as “demand shaping.”
Principles and Key Concepts of ITIL Demand Management
Here are the principles and basic concepts pertaining to ITIL Demand Management that you need to consider:
1) Balancing Supply and Demand
In ITIL, the demand arises through consumption while supply is delivered through production. This cycle can function smoothly only when the service assets have sufficient capacity. A core element of Demand Management is understanding potential demand and assessing its impact on service assets.
2) Leveraging Service Assets
Balancing supply and demand require the alignment of service assets with changing business needs. A clear mechanism must be in place to scale investment and resources when necessary. Service Management actions include:
1) Identifying relevant services via Service Portfolio Management.
2) Measuring business activity patterns.
3) Defining appropriate architectures for specific demand levels.
4) Ensuring capacity and availability planning supports timely, effective service performance.
5) Managing and tuning performance of service assets to adapt to demand variations.
3) Managing Demand Across the Lifecycle
For Demand Management to be effective, it must operate consistently across the entire ITIL service lifecycle. It cannot be left to processes solely at individual stages. Without ongoing coordination, demand will only be addressed reactively. This will reduce efficiency and bring on the risks of service disruptions.

The ITIL Demand Management Process
The following activities form the foundation of the ITIL Demand Management process:
1) Pattern of Business Activity (PBA)
The PBA reflects the organisation’s dynamics, including its interactions with customers, suppliers, partners, and other stakeholders. It helps service providers anticipate fluctuations. It helps ensure that resources are aligned with the business demands at the right time.
2) User Profiles (UP)
Each user profile corresponds to specific roles and responsibilities and may be linked to one or more PBAs. These profiles are designed through predefined activity patterns. By mapping demand through UPs and PBAs, the services, service levels and assets can be tailored to match user expectations.
3) Activity-based Demand Management
Through tracking business activity patterns, future IT service demands can be anticipated with more accuracy. This approach aligns customer business goals with Capacity Management plans, thus minimising the risks of underperformance or service bottlenecks.
4) Creating Differentiated Offerings
Studying PBAs often reveals that performance requirements vary across different time periods or operational conditions. In response, collaboration with Service Portfolio Management helps design service packages that cater to changing business needs.
5) Managing Operational Demand
This involves influencing the demand when resources or services exceed their designed capacity. By applying demand-shaping techniques, service providers can prevent overloads and protect long-term performance.
Master your IT assets and take charge of the IT landscape. Learn how with our ITIL® 4 Practitioner: Service Configuration Management Training - Sign up now!
Benefits of ITIL Demand Management
Demand Management is a cornerstone of an organisation’s financial and operational strategy. Its benefits include the following:
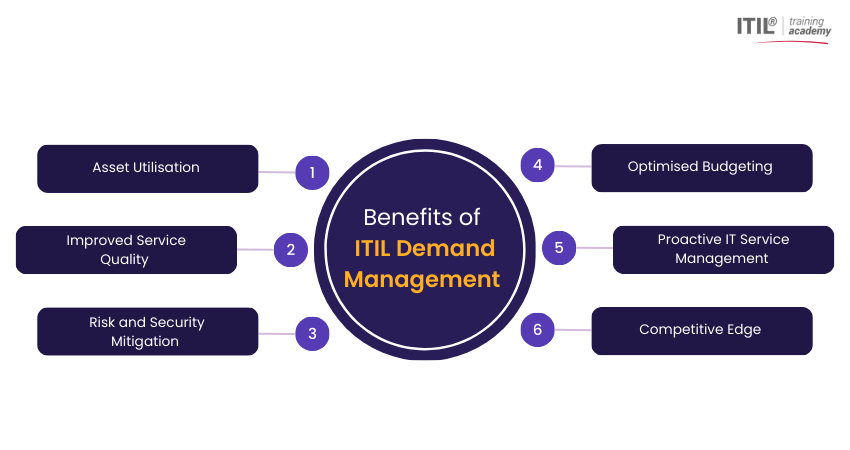
1) Asset Utilisation
ITIL Demand Management ensures that assets are used to their fullest potential, reducing waste and maximising value. By aligning asset deployment with demand cycles, you can prevent idle resources and improve overall efficiency.
2) Improved Service Quality
By using accurate demand forecasting, you can allocate resources effectively to maintain high service standards. This boosts collaboration and builds trust, thus helping the organisation establish a reputation for reliability.
3) Risk and Security Mitigation
With increased demand often comes increased cyber risks, making preparedness essential. Demand Management ensures that networks are resilient and capable of handling these threats while maintaining uninterrupted service delivery.
4) Optimised Budgeting
IITL Demand Management supports accurate budget planning, enabling wise allocation of resources and the reduction of unnecessary spending. This enables organisations to make informed financial decisions and align investments directly with business priorities.
5) Proactive IT Service Management
Demand Management shifts IT Service Management from a reactive stance to a proactive approach. This alignment ensures services evolve alongside business needs. It enhances long-term customer satisfaction and operational stability.
6) Competitive Edge
Accurate forecasting and reduced waste can help your business optimise pricing and service offerings. Such agility allows organisations to respond faster to market changes, outperform competitors and attract new opportunities.
Common Challenges in ITIL Demand Management
While ITIL Demand Management provides many benefits, it also presents specific challenges that organisations must address:
1) Limited Operational Visibility
Another difficulty arises from the lack of all-round visibility into business operations when Demand Management isn’t fully integrated. Information often has to be gathered in fragments, and service providers must juggle requests for new or modified services. They have to do this while ensuring a balance between immediate needs and long-term goals.
2) Addressing Diverse Business Needs
Reconciling the differing demands of multiple business units can be complicated. Without unified Service Management practices, it becomes harder to prioritise services, align them with strategic outcomes and showcase their role in overall value creation for the organisation.
3) Inaccurate Demand Forecasting
A major challenge is resource misallocation caused by poor demand predictions. Incorrect forecasts can lead to overspending without any real value. Customers may also struggle to understand which actions align with the service providers’ objectives.
IT success starts with smart strategy. Sign up for our ITIL 4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve Training now and strategise your next success story!
What Does Good Demand Management Look Like?
From transparent communication to avoidance of unforeseen expenses, here are the key characteristics of good Demand Management:
1) Transparent Communication
1) Clear communication between customers and the ITSM team is vital for efficient Demand Management.
2) The Business Relationship Manager acts as the key point of contact between customers and ITSM stakeholders.
3) Poor communication can negatively impact service quality, increase costs and disrupt the Demand Management process.
4) Effective processes help ensure that expectations are clearly communicated across all involved parties.
2) Streamlined Data Analysis Process
1) Understanding customer behaviour and anticipating the service volume is crucial for good ITIL Demand Management.
2) Demand varies over time, with some services peaking daily, weekly or seasonally. This requires detailed analysis.
3) Data Analysis continues during service transition and operation to compare predicted demand with actual demand.
4) A smooth pipeline collects relevant data, analyses feedback and informs decision-makers for accurate service design.
3) Avoidance of Unforeseen Expenses or Costs
1) A strong Demand Management process prevents unexpected costs from spiralling out of control.
2) Service delivery processes depend on accurate Demand Management to plan resources effectively.
3) If Demand Management fails, the entire ITSM framework risks going off-track.
4) When expectations are aligned and demand is controlled, organisational expenditures remain predictable.
Conclusion
ITIL Demand Management is like a strategic compass that guides IT services to meet business needs with greater precision. By mastering its principles, processes and overcoming its challenges, your organisation can turn unpredictability into opportunity. When done well, it balances resources, shapes demand and ensures that IT services consistently deliver growth in this ever-changing landscape.
Leading IT isn’t just about systems; it’s about future-ready vision. Craft your own vision with our ITIL® 4 Strategic Leader (SL) Training - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions?
No FAQs available for this blog.
Most Recent
Date - Feb 24, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026
Date - Feb 23, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics