Author-Maria Thompson
Last updated-Jan 2, 2026
Behind every reliable digital service sits a complex web of servers, applications, networks, and dependencies. But what can bring order to this complexity? The answer lies in the Configuration Management Database (CMDB), which acts as a map of an organisation’s IT environment. It records what assets exist, how they are configured and how they connect to deliver services.
In this blog, we'll explore What is CMDB, explain why it matters and show how it supports smarter, more resilient IT operations for modern businesses worldwide. So read on and gain a comprehensive insight into this ultimate blueprint for your tech infrastructure!
What is CMDB?
A Configuration Management Database is a central repository that records and manages details of the components that form an IT environment. It supports the organisation and visibility of systems, assets, and services across the IT landscape.
Within IT Service Management (ITSM), Configuration Management relies on a CMDB to monitor Configuration Items (CIs), which include any assets or components involved in delivering IT services. The CMDB captures key information such as CI attributes, relationships, dependencies, and configuration changes over time.

Features of a CMDB
Key CMDB features include the following:
1) CMDB Workspace: It offers a structured environment to view and analyse configuration items and their interactions.
2) Data Acquisition and Integration: It collects and consolidates data from multiple sources, such as discovery tools and sensors.
3) Relationship Mapping: It visually illustrates how CIs depend on and interact with each other, thus supporting operational insight.
4) Visualisation and Reporting: It generates clear diagrams, maps and reports that help the organisation understand how CI relationships support business services.
5) Centralised Asset Management: It maintains a single, reliable source of truth for all IT assets across the infrastructure.
6) Compliance Support: It enables organisations to demonstrate alignment with policies and regulatory requirements.
7) Access Controls: They define who can view or modify CMDB data, thus ensuring secure and controlled access.
8) Lifecycle Management: It supports tracking and managing assets throughout their full lifecycle, from deployment to retirement.
9) Root Cause Analysis: It provides critical configuration insights that assist in identifying underlying causes of service disruptions.
10) Risk and Change Management: It supplies accurate data to assess risks and plan changes with minimal service impact.
11) Incident and Problem Management: It helps technical teams investigate incidents and problems by referencing detailed asset and relationship information.
How Does a CMDB Work?
Here’s how CMDB solution works:
1) Automated Discovery: Modern CMDBs use automated discovery tools to scan the IT environment continuously, identifying new components and detecting changes without manual input.
2) Real-time Visibility: The CMDB maintains an accurate, near real-time view of the IT landscape.
3) Asset and Dependency Tracking: It captures not only assets but also their relationships and dependencies.
4) Impact Analysis: Relationship mapping enables IT teams to assess impact before making changes, such as identifying dependent applications and services prior to decommissioning a server.
5) Current and Historical Insight: The CMDB acts as both a live snapshot and a historical record of the infrastructure. It tracks configuration changes over time.
6) Automated Asset Updates: When new assets are introduced, the CMDB automatically records them, links them to related components, and updates the inventory.
7) Change History and Analysis: Detailed change histories support audits, troubleshooting and root cause analysis by highlighting when and where configuration changes occurred.
Drive digital success with a green mindset with our ITIL® 4 Specialist: Sustainability in Digital and IT Training ITIL® SDIT - Sign up now!
Benefits of CMDB
Here are the six major benefits of employing a Configuration Management Database:
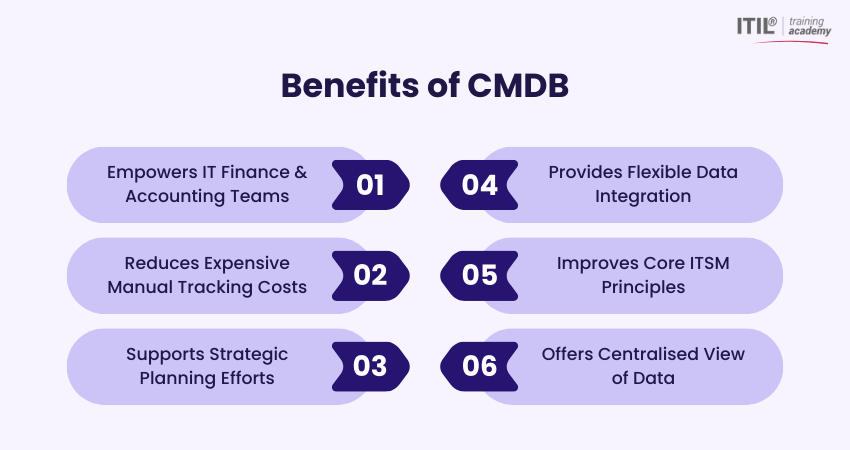
1) Accounting
A CMDB helps IT Finance and Accounting teams track details about configuration items, licensing and service codes. This helps with accurate cost allocation, inventory billing and better financial reporting across IT assets.
2) Cost Savings
By consolidating asset and CI data into one system, organisations can reduce expensive manual tracking and minimise duplicate tools. It can lower CMDB vendor costs and increase operational efficiency.
3) Planning
CMDB data supports strategic planning efforts such as enterprise architecture, Capacity Management and service roadmaps. Additionally, it helps understand how changes impact the environment before implementation.
4) Data Integration
Modern CMDBs integrate information from across IT systems, assets, and tools to give a single, organised view of configuration data and dependencies. This improves context and consistency.
5) Operating
CMDBs improve core IT Service Management practices, such as change, incident and Problem Management, by linking configuration items to incidents and supporting processes. This helps with faster resolution and reduced risk.
6) Centralised View of Data
A CMDB provides a unified source of truth by storing hardware, software and their relationships in one centralised repository. This delivers complete visibility into the IT environment’s configuration and interdependencies.
Challenges of a CMDB
Most failures in implementing CMDB initiatives successfully stem from common, avoidable issues that typically fall into these six areas:
1) Culture
Organisational culture plays a decisive role in CMDB success. Technology alone cannot deliver value without the people adopting the processes behind it. People and process challenges outweigh technical ones, and CMDB initiatives are no exception.
2) Relevance
With CMDBs labelled as a single source of truth, some organisations overload them with unnecessary data. A CMDB must instead focus on relevant, high-value information that directly supports processes such as change and Incident Management.

3) Centralisation
A common misconception is that all the asset data must physically reside in the CMDB. The truth is, effective CMDBs federate data from specialist tools rather than replacing them. For example, financial data is better maintained in IT Financial Management systems, while licence details belong in Software Asset Management tools.
4) Accuracy
Maintaining accurate CMDB data is a widespread challenge. Infrequent discovery scans, limited automation and reliance on manual updates often lead to outdated records. Manual inputs still have a role for non-discoverable items, provided they are well governed.
5) Process
Some organisations view CMDBs as tools suited only for legacy infrastructure, which leads them to overlook their value in modern Cloud-based and software-defined environments. Focusing on terminology rather than outcomes can restrict progress.
6) Tools
Selecting the right CMDB tool is critical. Many failures result from using rigid systems designed for static, physical assets that struggle with dynamic environments. Successful CMDBs support modern asset types and integrate easily with other tools.
Every asset counts. Learn how to manage them smartly with our comprehensive ITIL® 4 Specialist: IT Asset Management Training - Register now!
CMDBs and ITIL
The IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Service Management framework defines clear guidelines for Configuration Management. Under ITIL guidance, Configuration Management focuses on four core areas:
1) Discovery: It involves identifying and documenting configuration items (CIs) that should be recorded in the CMDB.
2) Security: It protects configuration data by ensuring only authorised individuals can make changes.
3) Reporting: It maintains accurate and consistent CI status information through regular updates.
4) Auditing: It validates data accuracy by conducting audits and formal reviews.
IT Asset Management (ITAM) vs Configuration Management
Here are the main differences between ITAM and Configuration Management: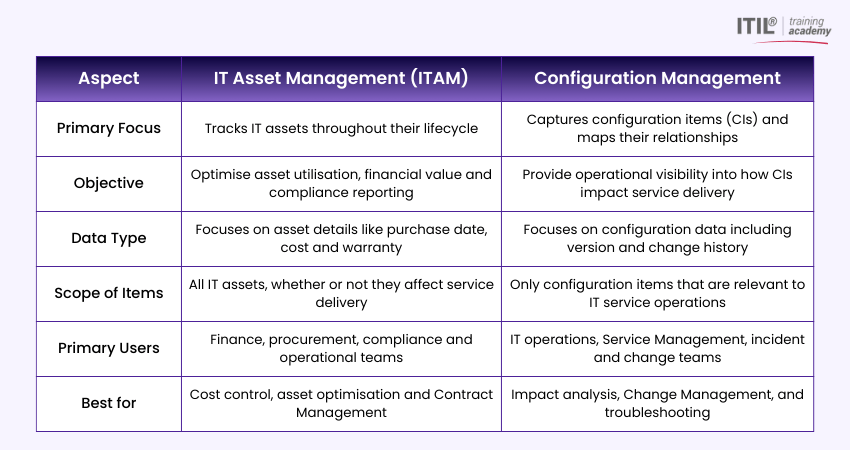
What are CMDB Best Practices?
Sustaining an effective CMDB requires careful planning and continuous oversight. You can realise far greater value from Configuration Management with these proven best practices:
1) Define Clear Objectives First: Establish specific business and technical goals before implementation. This direction shapes tool selection and process design.
2) Adopt a Phased Approach: Start with high-impact services and critical infrastructure, then expand gradually.
3) Prioritise Relationships Over Asset Lists: Focus on capturing how components interact and depend on each other. This context delivers the greatest operational value.
4) Leverage Automated Discovery: Use automation to keep data accurate and reduce manual effort, while validating results where required.
5) Align With Change Management: Integrate the CMDB with change processes. This will ensure that approved updates are consistently reflected as the environment evolves.
6) Assign Clear Ownership: Designate responsibility for different CI types to maintain accountability.
7) Validate Data Regularly: Perform ongoing checks between discovered and recorded configurations to identify and resolve inconsistencies quickly.
8) Deliver Role-based Training: Tailor training to show how the CMDB supports specific responsibilities. This improves adoption and engagement.
9) Track and Communicate Value: Measure improvements such as faster incident resolution, fewer change failures and stronger compliance to maintain stakeholder support.
Real-world Applications of a CMDB
Here are some exciting real-world applications of CMDB:
1) Change Management Impact Analysis: Before upgrading a database server, a CMDB shows which applications, APIs and business services depend on it.
2) Incident Management and Faster Resolution: When a critical application goes down, the CMDB helps service desk teams trace related servers, network devices and middleware.
3) Problem Management and Root Cause Analysis: Repeated performance issues can be analysed using CMDB relationship data to identify a common failing CI, such as a shared storage system or load balancer.
4) IT Asset and Service Visibility in Large Enterprises: In complex environments with thousands of assets, a CMDB provides a single view of how hardware, software and cloud resources combine to deliver proper services.
5) Cloud and Hybrid Infrastructure Management: For organisations using on-premise systems alongside AWS or Azure, a CMDB maps relationships between virtual machines, containers and databases.
6) Service Impact Assessment During Outages: If a network switch fails, the CMDB identifies which business services and user groups are affected.
7) Merger and Acquisition IT Integration: During mergers, a CMDB helps map overlapping systems, shared dependencies and integration risks. This reduces disruption during IT environment consolidation.
Conclusion
Learning What is CMDB is vital for IT professionals because a Configuration Management Database transforms scattered IT components into an intelligible ecosystem. By revealing how assets, services and dependencies interact, a CMDB helps teams manage change confidently and resolve incidents faster than ever. In an evolving digital world, a well-maintained CMDB becomes the backbone of resilient IT Service Management.
When IT challenges evolve, so should you. Upgrade your mettle with our comprehensive ITIL®4 Extension Modules Training - Sign up now!
Most Recent
Date - Jan 6, 2026
Date - Jan 5, 2025
Date - Jan 6, 2026





 Back to
Topics
Back to
Topics
























